Τομείς
Το τμήμα σύνθετων υλικών της CFT ασχολείται με κατασκευές κομματιών από σύνθετα υλικά (ανθρακονήματα, υαλονήματα, Kevlar) αλλά και συναρμολόγηση δομών που απαρτίζονται από επιμέρους κομμάτια είτε είναι κατασκευασμένα από σύνθετα υλικά αποκλειστικά είτε περιλαμβάνουν και μεταλλικά στοιχεία ή αντικείμενα τρισδιάστατης εκτύπωσης.
Η συνεργασία μας με ένα ευρύ και εξειδικευμένο δίκτυο συνεργατών και προμηθευτών μας επιτρέπει να προσφέρουμε ολοκληρωμένες λύσεις για εφαρμογές που απαιτούν συνδιασμό διαφορετικών υλικών.
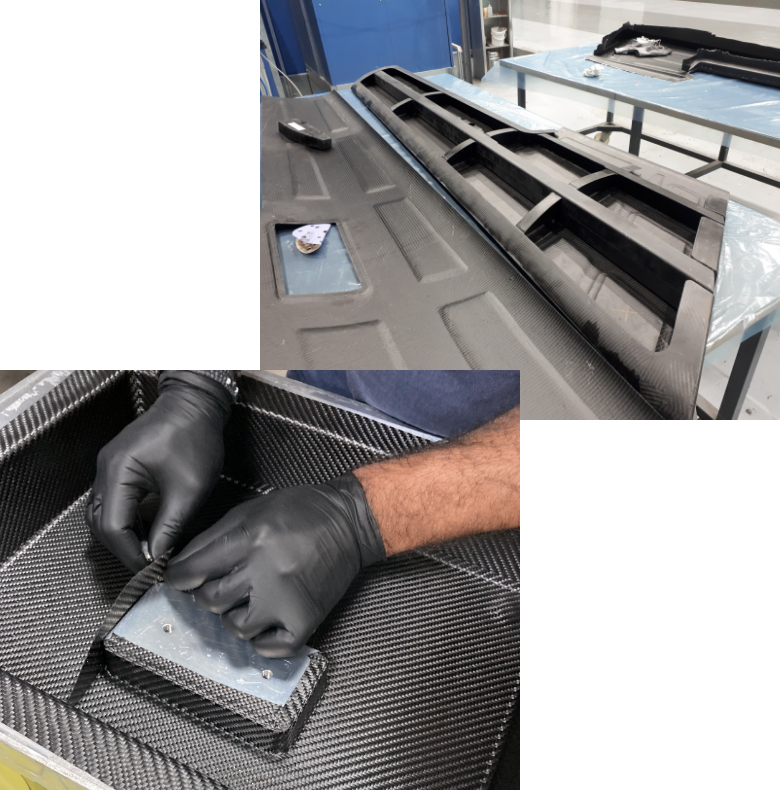
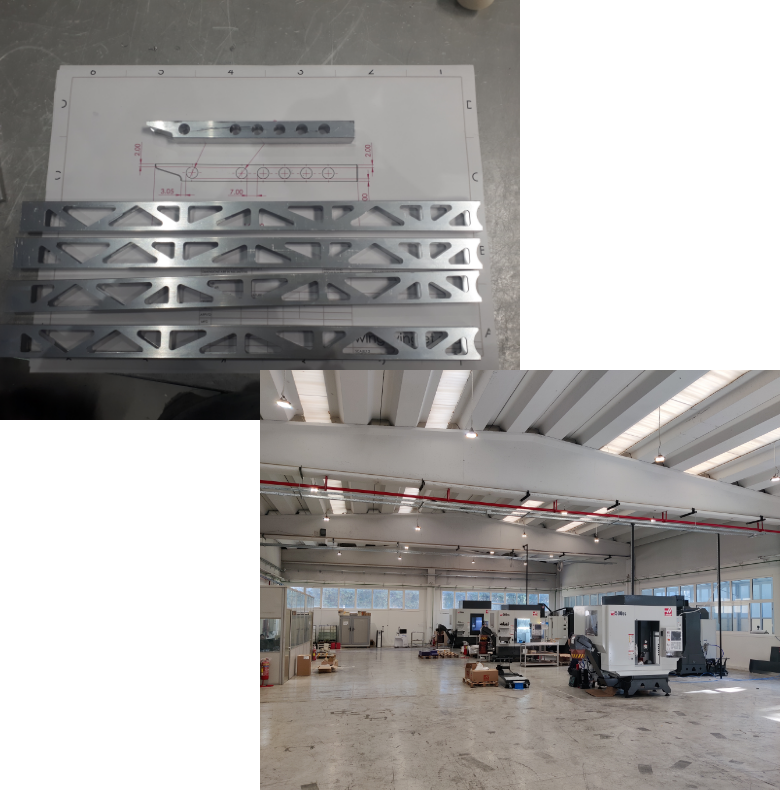


Η CFT αποτελεί προσφέρει υπηρεσίες μηχανουργικών κατεργασιών μετάλλων χρησιμοποιώντας προγραμματιζόμενες εργαλειομηχανές CNC.
Επιτυγχάνουμε απαράμιλλη ποιότητα με προσοχή στη λεπτομέρεια, καθώς και τις ανταγωνιστικότερες τιμές της αγοράς.